Under the Shadow of the Extreme Case
On his first day in office, Los Angeles DA George Gascón rolled out a suite of blanket bans against some severe punishments. The ensuing years have been a crash course in the politics of reforming prosecution.
Piper French | January 24, 2024
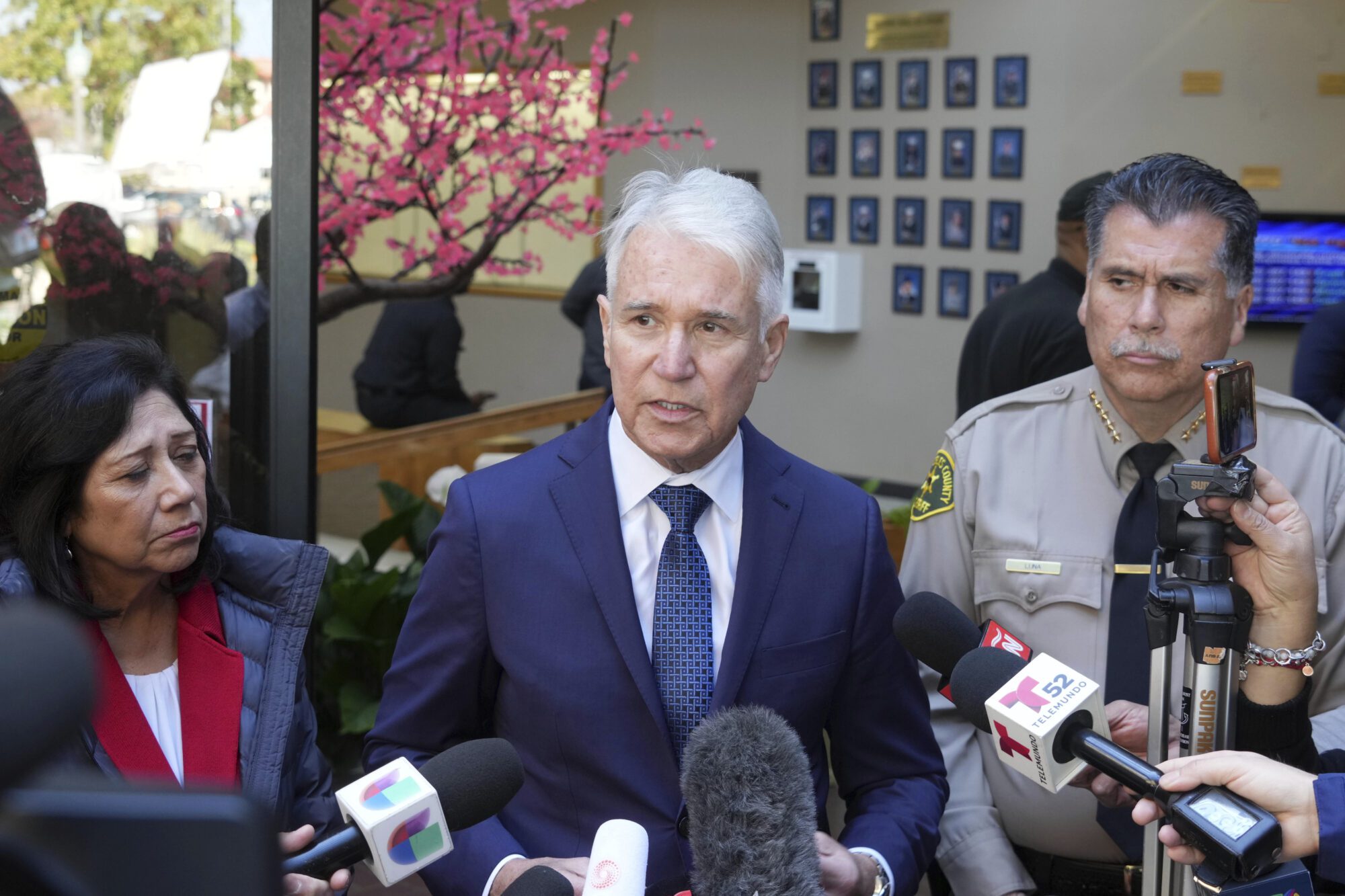


In December 2020, on the eve of taking the reins as the district attorney of Los Angeles County, George Gascón was up late trying to make a decision. He’d been elected weeks earlier on promises to change Los Angeles’ approach to criminal punishment, but he was hesitant on how much to shake up the system. “10, 11 o’clock at night, the night before I was being sworn in, I’m looking at two versions of what I’m going to say,” Gascón recalled in a recent interview at his office in Downtown LA. His first speech articulated a more incremental approach, but the more he looked at it, the more he became convinced that it would risk “business as usual.”
He chose the second speech.
The following day, Gascón announced a sweeping set of categorical, or ‘blanket’ policies, his office would adopt: no death penalty, no charging minors as adults, no life without parole sentences. Not rarely, or selectively—never, under any circumstances. Perhaps most consequentially, he vowed that prosecutors in his office would not seek enhancements, special circumstances that can add decades to someone’s sentence and affect tens of thousands of cases each year in Los Angeles County.
Prosecutors are typically reluctant to delineate such clear-cut policies, preferring to protect the boundless discretion of their office. Even those who vow reform tend to merely promise to deprioritize certain practices without ruling anything out. But Gascón told me that it was important for him to draw clear lines in the sand, in part because he knew that he’d be walking into an office whose management team largely opposed his plans. “I wanted to make sure that this was going to be just not a bunch of political promises—this was going to be a real thing,” he said.
Nearly immediately, the new DA found himself under fire, including from staff in his office who bristled at being told not to use some of their regular tools. Almost as quickly, he announced a tweak to his enhancements policy, allowing exceptions for hate crimes and offenses against children and the elderly. And that was just the beginning. Many of the biggest inflection points of Gascón’s first term have revolved around the use of blanket policies: one court battle after his own deputies filed suit claiming that his directive to not seek enhancements violated the law, one protracted media storm involving a case that seemed to challenge the principle of never trying young people as adults, and two fizzled recall attempts by adversaries who said he was neglecting the duties of his office.
Now, Gascón is defending his seat against 11 challengers, nearly all of whom are running to his right in the March primary. (The top two candidates will head to a November runoff unless someone clears 50 percent of the vote.) Many of his opponents are attacking the very idea that a DA should ever issue categorical policies. In fact, a number of them have contested his approach ever since 2020. The field includes four line prosecutors working in his office, several of whom are highly involved in the union that sued him and one who says she was demoted for questioning his directives; and a former attorney at the firm that filed the lawsuit.
At first glance, blanket policies might seem like an intuitive tool for reform prosecutors because they both embody a clear vision of change and help to enact that vision. “They’re actually very useful, smart policies to implementing what we care about, which is a less racist, more fair system where also we can put more resources into very, very serious cases,” said Jessica Brand, founder of the Wren Collective, a national organization that researches criminal legal policy and helps advise reform prosecutors.
But Brand said she’s nonetheless hesitant about recommending such policies: “They’re latched onto in these hyper political ways.” Blanket directives like Gascón’s tend to become lightning rods for controversy, especially given that so much of criminal legal policy—and debate around that policy—in the U.S. is defined by the specter of extreme cases.
One of the most indelible examples of this dynamic in modern American politics happened just across town from the Los Angeles DA’s office.
During a 1988 presidential debate held at UCLA, Democratic nominee Michael Dukakis, a lifelong opponent of the death penalty, was asked if he would change his mind about capital punishment if his own wife, Kitty, were raped and murdered. His immediate answer—that he wouldn’t, given his deeply felt principles on the matter—is widely considered to have harmed his presidential bid; it remains seared in the minds of a generation of political observers, a cautionary tale about the perils of ruling anything out when it comes to criminal punishment.
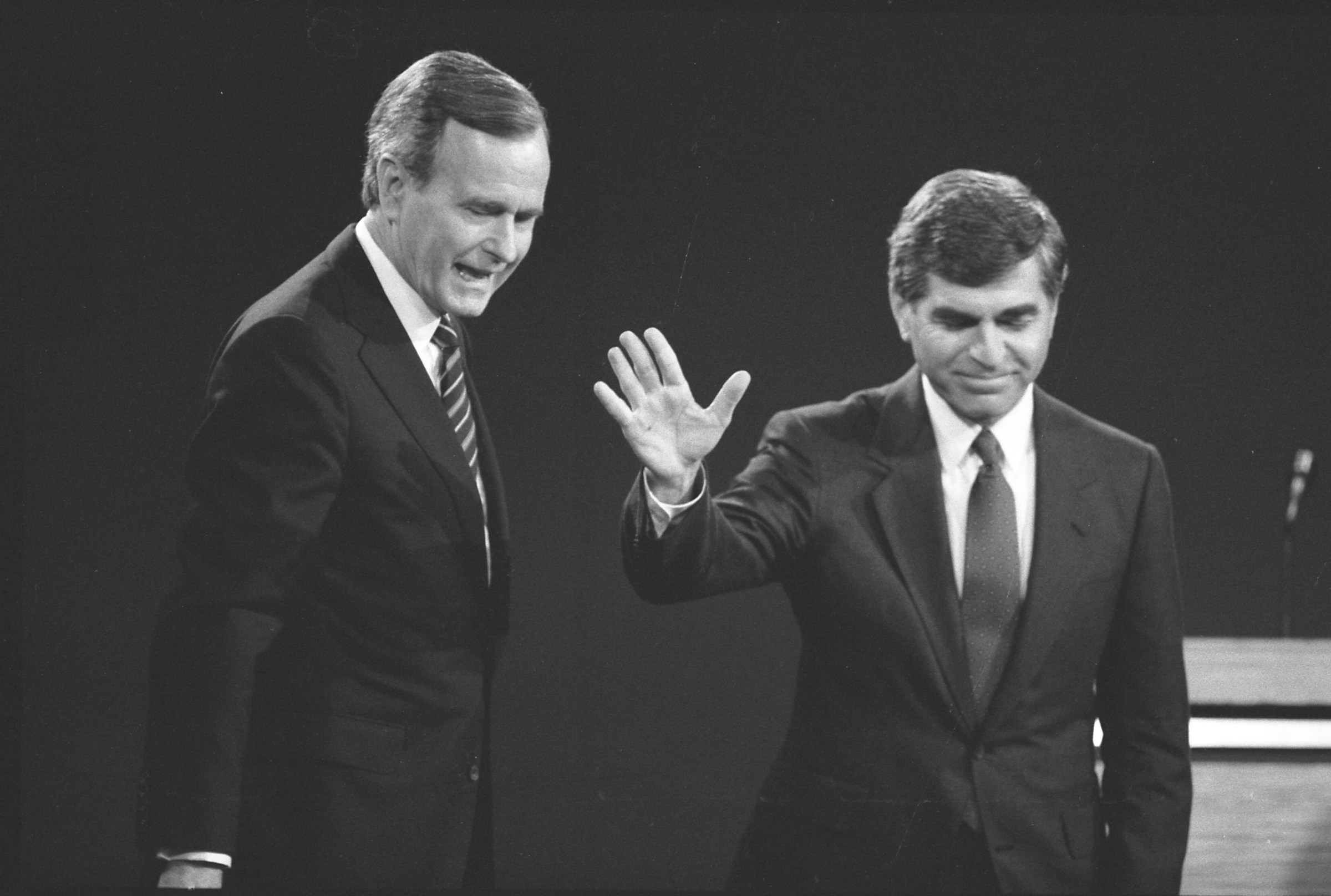


Over 30 years later, Gascón ran on the gamble that the politics of crime had changed enough for him to rule out quite a bit more than just the death penalty, and he won in 2020 after making blanket promises as part of his campaign pitch. But the ensuing years only raised the stakes of that gamble, leading the DA to hedge in certain ways and double down in others. As he embarks on a difficult reelection campaign, I wanted to understand what Gascón’s tenure has revealed about the politics of transforming prosecution, especially in a place as vast and complex as Los Angeles. How do you set about making big changes to an entrenched system without sparking so much resistance that your ambitions founder? What does it take, in other words, to dispense with business as usual?
To understand why a reform DA would insist on a blanket policy despite the political risks, you first have to understand the status quo they’re fighting against. “This is an arcane system, and it’s not going to go gently and quietly into the night,” Cynthia Roseberry, acting director for the ACLU’s Justice Division and a former public defender, told me. “We’ve got to be bold in our strokes to change it.”
For reform DAs like Gascón, blanket policies are an effort to disengage from practices that they consider simply unconscionable: outdated, racist, overly harsh, or morally dubious. Gascón cites data showing that the death penalty is riven with errors and racial bias. He points to the fact that young people sent into the adult system can spend decades in prison for a mistake they made as a teenager. And he has underscored that sentencing enhancements, a product of the tough-on-crime era, can add many years of incarceration onto whatever baseline punishment has been determined to fit the underlying crime. “Do we send somebody to prison for way beyond their natural life, or do we send them for a period of time where they may be able to redeem themselves and come back?” Gascón asked me.
Blanket policies can put clear guardrails around a DA’s charging decisions, instead of them telling the public: just trust me. If you believe that the state shouldn’t be in the business of taking a life or that young people’s developing brains leave them fundamentally unable to grasp consequences the way an adult can, there’s no sense in judiciously applying the death penalty or charging juveniles as adults, the thinking goes—it simply shouldn’t be done at all.
“When we think about removing something like enhancements, what we’re also saying is we know that they’ve been used improperly and there’s not a way to correct them in isolation,” said Roseberry. Mona Sahaf, who runs the Vera Institute’s Reshaping Prosecution Initiative, thinks that “it’s a big opportunity to shrink the footprint of the system.”
Reformers also make the case that prosecutors have had a key role in exacerbating mass incarceration. Discretion is the lifeblood of their trade, but historically, prosecutors have almost always used that freedom to move in one direction—towards harsher punishment, even above and beyond what the law requires. Over and over again, they come down on some people harder than others: 45 percent of people serving a life sentence in California under the Three Strikes law are Black, as Gascón’s enhancements directive noted. Maria Gonzalez, the legal clinic coordinator at Los Angeles’ Youth Justice Coalition, has a loved one doing 100 years on an enhancement case. “That life is done. It’s gone,” she told me flatly.
Other prosecutors who say that they share Gascon’s opinions about the death penalty, or that sentencing enhancements are broken, still prefer to say they’ll assess each case on its own, rather than draw a clear line in the sand. But to organizers like Melina Abdullah, a leader of Black Lives Matter’s Los Angeles chapter, this is just a way “to not make any commitments.”
“You can’t just make decisions on a case-by-case basis,” she told me. “You have to have a set of legal principles that you adhere to.”


After all, DAs aren’t running around trying cases themselves—rather, they oversee large offices of deputies responsible for the day-to-day work of prosecution, who can easily ignore vague principles from up top. In fact, given that the professional norms of prosecutors tilt towards punitive sentencing, reform prosecutors have found themselves undermined by staff resistant to carrying out their changes.
Announcing blanket policies, then, is a way for reform DAs like Gascón to use the power they do have to limit the power of their own office, and to tie the hands of the vast bureaucracies they oversee. Prosecutors don’t have the ability to directly stop police from racially profiling young men of color, or to edit the penal code, or to rectify the socioeconomic inequalities that can lead to gang involvement. What they can do is order their own staff to stop using gang enhancements.
Or can they? Less than one month after Gascón took office, his line prosecutors took him to court, contending that his enhancements directive was forcing them to break the law. Legislators passed the STEP act, which established sentencing enhancements for gang affiliation, and Californians approved a “three strikes and you’re out” sentencing scheme; the lawsuit argued it simply wasn’t in Gascón’s power to forbid his deputies from using those tools. Gascón replied that voters elected him to upend the status quo, and that his role allowed him to direct his own staff.
In February 2021, a judge ruled that Gascón did not have the authority to bar his prosecutors from seeking enhancements for prior strikes, or serious felony charges. As long as California’s “three strikes” law was on the books, it wasn’t up to him whether to enforce it. But the judge’s decision did leave him free to bar his prosecutors from seeking other forms of enhancements in new cases. Gascón argues that this ruling wasn’t a major blow to his plans because it only affected a share of enhancement cases.
“Quite frankly, it’s a very small piece, not only of the policy, but of the work,” he told me. At that point in 2021, the bulk of his vision remained intact.
The backlash to blanket policies is politically and geographically contingent. In red states, even the appearance of one has led to preemption or removal by state officials, meaning that DAs trying to do things differently are often forced to be a bit cagier about their plans, while prosecutors in blue states tend to have more leeway.
In 2017, Orlando’s prosecutor, Aramis Ayala, was taken off some high-profile murder cases by the Florida governor after she announced she would never seek the death penalty. In San Francisco, meanwhile, former DA Chesa Boudin encountered comparatively tepid criticism for his ban on death penalty cases, in part because two predecessors—Gascón and Kamala Harris—had already paved the way. “It was well within the heartland of San Francisco politics,” Boudin, who now runs UC Berkeley’s Criminal Law and Justice Center, told me.
In liberal Los Angeles, Gascón’s death penalty ban has also not been seriously contested, even though the county lacks the precedent that San Francisco had; his predecessor, Jackie Lacey, was notorious for her embrace of capital punishment, and helped make LA County one of the nation’s leading counties in handing out death sentences. But Gascón went further. By attempting to address lengthy sentences for people who commit violent crimes, he struck what has long been a third rail in reform debates, even among people who agree that mass incarceration is a problem: questioning very lengthy sentences for people who commit violent crimes.
The U.S. has often fashioned its approach to punishment in direct reaction to especially heinous or high-profile crimes—California’s ‘three strikes’ law, for instance, was motivated by the abduction and murder of nine-year-old Polly Klaas—and these crimes have animated debates around sentencing policy in a more ambient way, too. We have no shortage of infamous cases to draw from—serial killers, mass murderers, bizarre cases like Charles Manson or the Unabomber—and these people tend to loom very large in the popular imagination, even as they represent a microscopic percentage of Americans who commit crimes. This has meant that extreme outcomes—sentences of decades or even hundreds of years—have become commonplace, far more so than the extreme offender they were initially designed for.
Today the specter of the “worst of the worst” continues to haunt criminal legal debate, often putting politicians who favor major policy upheavals on the defensive, like Dukakis answering Bernard Shaw’s question in 1988 in front of tens of millions of Americans. This is particularly fraught within the juvenile justice system, where the increasingly popular slogan that we should treat children as children, in accordance with newer research showing that brain development continues into the mid-20s, exists alongside the possibility of truly extreme cases.
In Sahaf’s time working with reform prosecutors at Vera, she has observed that “it’s very difficult to make an absolute pledge never to charge a child as an adult and then carry through on it, because you see these exceptions happen…children do sometimes commit really atrocious crimes.” And eventually just such a case would land on Gascón’s desk: Hannah Tubbs.
Tubbs’s case seemed to span the gamut of aggravating factors: here was someone who had sexually assaulted a child in a restaurant bathroom stall less than a year before turning 18, who was 26 by the time she was caught and facing punishment, who had already racked up an extensive criminal record, and who mocked the victim and expressed no remorse. “Nothing is ever unique, but it was as close to unique as you could [get],” Gascón told me. But he added that there were mitigating circumstances, too. His commitment to keeping the case in the juvenile system led to internal clashes, and then public opprobrium after jailhouse recordings of calls between Tubbs and her father were leaked to Fox News.
“This clearly shows you the dangerous aspect of the blanket policies of George Gascón,” Jonathan Hatami, a prosecutor in the DA’s office and frequent critic who’s now running against him, told the LA Times—which, along with other local media, covered the case extensively.
Facing the biggest fracas of his tenure, Gascón announced in February 2022 that he would alter his directives on life without parole sentences and charging juveniles as adults: instead of total bans, he was establishing two committees to consider “extraordinary” cases that might merit such special circumstances. Each committee would be staffed by three senior advisors, including one who publicly stated she didn’t agree with his about-face.
This approach, his office said, would “create a different pathway for outlier cases, while simultaneously creating protections to prevent these exceptions from becoming the rule.”
These tweaks may seem minor, since “extraordinary” cases are by definition rare and since Gascón created a structured process to evaluate them. But to some, their vague quality signaled a worrisome retreat from the principles the DA had run and won on.
For the ACLU’s Roseberry and local advocates like those at the Youth Justice Coalition, even one minor charged as an adult is one too many. “The idea that we would approach them in any respect as irredeemable is a frightening prospect,” said Roseberry. “These children come to us having been shaped by circumstances and environments that are beyond their control.”
Other reform DAs have tried for a similar balance as Gascón: Boudin’s sentencing directive in San Francisco, for instance, created a presumption against enhancements but left room for them in “extraordinary circumstances,” as long as he or a deputy signed off. “From a legal standpoint, we were on stronger ground by writing into the policy discretion to make exceptions,” he told me. (Boudin did maintain a blanket prohibition against charging juveniles as adults throughout his two and a half years in office.)
Still, Youth Justice Coalition communications director Emilio Zapién stressed that using edge cases to guide criminal legal policy making is destructive to the chances of the young people the Youth Justice Coalition works with. “For every really horrific case, like the one you’re talking about, the Tubbs case, there are 15 to 20 others [that show] transformation,” he told me.
Zapién added that he found the whole debate around Tubbs to be cynical: “The folks that are arguing for more criminalization and incarceration of young people of color after the mainstream media sensationalizes one case as a political tactic… those folks already had those beliefs before.”
At the time of the Tubbs case, Gascón had already weathered one recall campaign motivated by aspects of his categorical policies. One of the public faces of the recall was a woman, Desiree Andrade, whose son Julian had been brutally murdered. Under Lacey, his killers faced the death penalty or life without parole; once Gascón took office, those options were off the table. The words “Gascon [sic] REFUSES to prosecute juveniles as adults under any circumstances, even rape, murder or other heinous crimes, even if days shy of turning 18” were front and center on the campaign’s website.
That recall attempt imploded after organizers failed to garner enough money or signatures–but they swore they’d be back, and some recall proponents took up the Tubbs case as a rallying cry. The second recall campaign that resulted also fizzled out about a year later. Ironically, it’s been the intensity of the opposition to Gascón, more than anything else, that has vindicated what many of his allies have said all along: prosecution is political.
Now the energy behind those efforts has been channeled into the upcoming election, with a number of Gascón’s loudest critics and recall supporters returning to run against him.
Nathan Hochman, a former Republican candidate for California attorney general, writes on his campaign website that Gascón’s blanket directives “demonstrate distrust in his prosecutors” and promises to restore prosecutorial discretion. His website names the elimination of blanket policies as a crucial component in his “blueprint for justice.”

John McKinney, a prosecutor in the DA’s office, said at an October debate that he’d “repeal and replace” every directive Gascón announced on his inauguration day. Hatami, the frequent critic, has said that “blanket policies should all be revoked,” telling Los Angeles Daily News “I believe in discretion.” Eric Siddall, another prosecutor in Gascón’s office and the former vice president of the deputy DA union, has also vowed to make the issues targeted by most of Gascón’s blanket policies subject to a “case-by-case analysis” instead. Maria Ramirez, yet another prosecutor in the office, has used similar language.
I reached out to the campaigns of a handful of the candidates for their thoughts on blanket policies. None responded by the article’s deadline. Jeff Chemerinsky’s campaign reached out after publication to say that Chemerinsky, a former federal prosecutor, would never seek the death penalty as DA, but that he would eschew other blanket directives.
Siddall, who has also insisted he is not opposed to progressive reform while criticizing Gascón for taking a “defendant-centered approach,” has made the same key concession to Gascón’s model, vowing to forgo the death penalty. Other candidates, meanwhile, have not ruled it out. It may not be to his advantage, but Gascón’s blanket policies set the terms of the debate.
Gascón has made more than a few political calculations of his own over his three years in office. As he approaches his first reelection test in March, he has kept in place some of his initial blanket directives, like his commitment to never seek the death penalty. During the tenure of his predecessor Lacey, 22 people were sentenced to death in LA, all of them people of color, but Gascón has never tried. His administration has also worked to resentence people who are already on death row to life without parole; his office told me it has secured that change for 29 people as of this week.
Meanwhile, the DA has altered some directives to define a process for considering “exceptional” cases, while preserving the central presumption of the policy. He has walked farther back from others, maintaining the goal of avoiding certain enhancements but without clear guidelines. And he’s been barred by the courts from pursuing still others.
This convoluted landscape reflects Gascón’s concessions to his critics from the right, to be sure. But his case to progressives has also evolved: His record shows, he argues, that blanket policies altered by carve-outs can also accomplish his decarceral goals. “Do I think this has made a difference?” he asked me when we spoke. “I think it’s made a tremendous difference.”
Gascón softened his blanket prohibition against charging minors as adults, for instance, but this has not opened the floodgates to adult prosecutions.
As a result of his original policy, Gascón said that hundreds of teenagers per year who might otherwise have been sent to an adult prison are now being treated in the juvenile system. To Gonzalez, who spends her days in court advocating for young people on behalf of the Youth Justice Coalition, the change has been palpable.
“LA County has made so much progress on helping our youth,” she said. “I’ve seen young people be under diversion and continue to go to school, graduate from school. Last year, we had two graduates that could have easily just been in a cell.” (Like her colleague Zapien, Gonzalez disagrees with Gascón’s decision to modify this policy).
Since Gascón modified his blanket prohibition in February 2022, the Juvenile Alternative Charging Committee had recommended that ten cases be transferred to adult court, according to the DA’s office. In the first transfer hearing to take place, the judge, J. Christopher Smith, actually overrode the committee, ruling that the teenage defendant wasn’t beyond rehabilitation and noting that he had cognitive deficiencies and a history of childhood abuse. The ruling echoed Gascón’s initial absolute commitment to the possibility of personal transformation even in cases where a young defendant had done something heinous; in doing so, Smith brought into sharper relief Gascón’s decision to retreat from that principle.
Gascón told me that he actually agreed with the judge’s decision. But he also defended his office’s charging committee, saying they may have been influenced by the gravity of the crime, a double murder, and invoking the value of outsourcing these evaluations to an independent body. “I gave the committees full freedom to decide,” he told me.
Separately, he called it “affirming” that state law had nearly caught up to his December 2020 blanket policy: In 2022, the California legislature raised the bar to try minors as adults, reflecting the changing consensus on juvenile culpability. (Gascón wrote a letter in support of that effort).
Similarly, Gascón set up a charging committee tasked with determining whether a case merits a possible sentence of life without parole, and this committee has given prosecutors the go-ahead to seek that sentence some 23 times since February 2022, according to information gathered on the DA’s website. The office has applied a “special circumstances” enhancement, which requires a sentence of life without parole in the event of a conviction, in two recent high-profile and especially gruesome cases: a man who allegedly serially targeted and killed homeless people, and the son of a famous Hollywood agent who is accused of killing and dismembering his wife and her elderly parents.


Gascón may have gotten what he wanted out of these cases: They are being widely covered in local media, but seemingly no one has invoked them in order to criticize the DA for being soft on crime. By opening the door to some life without parole sentence in high-profile instances, the DA had perhaps freed himself up to avoid that sentence in the vast majority of cases with far less scrutiny or blowback.
But just how far can he take this approach? The judge who ruled on the deputy prosecutors’ lawsuit in 2021 gave Gascón carte blanche to maintain his initial blanket policy barring other sorts of new enhancements—special allegations that would add on extra time for gang involvement or the presence of a weapon, for example. The DA’s office says it has maintained a blanket prohibition on gang enhancements.
But on gun enhancements, Gascón has retreated from his initial categorical policy in a murkier way. In November, he told me that his office had been adding gun enhancements on a case-by-case basis, allowing line prosecutors to seek them if they get management approval.
“We are selectively using those enhancements but it’s being done, again, much more thoughtfully,” Gascón said.
I later asked Gascón’s chief of staff, Tiffiny Blacknell, why Gascón retreated from this blanket policy voluntarily. “It’s reasonable that there should be some exceptions to some of these directives, with the exception of the death penalty,” she said, adding that the DA had over time erected a management structure that he trusted to carry out his vision. “We’re using a scalpel, not a sledgehammer.” The office does not have a written policy governing when it’s appropriate for prosecutors to seek these enhancements. Blacknell said bureau directors make the final decision based on factors such as the severity of the crime and past criminal history.
On this front at least, the DA’s current stance sounds a lot more like the “case-by-case” rhetoric of his challengers. This risks a return to the starting point that local progressives hoped to get away from: just trust me, I’m the one who can use this tool wisely.
And that argument, Gonzalez said, wouldn’t slide with the people who elected him in the first place. “The community is bigger than the pushback he’s getting right now,” she told me. “The community is gonna stand up and say, ‘I don’t believe you.’”
Gascón says it’s easy to distinguish his commitment to reform from opponents who only pay lip service to it during campaign season, pointing to his record in office.
For organizers who work closely on policing, prisons, and sentencing in Los Angeles, there is a continuous need to decide whether they buy the DA’s revised case for change. Are his carve-outs a strategically savvy response to the backlash, or are they a retreat to punitive conventions? What’s the line between preserving some space for extraordinary cases and mirroring old paradigms of boundless prosecutorial discretion? In that ongoing assessment, many are balancing their frustration over Gascón’s walkbacks with an awareness of what he’s up against—what it takes to change an intractable system under the ever-present specter of Michael Dukakis.
“I’m never a fan of a prosecutor because I think the system is fundamentally set up against Black and brown and Indigenous and poor people,” Abdullah told me. But she noted that the DA has pursued goals she sees as critical, including prosecuting law enforcement officers who engage in violence or corruption. “I think what he’s demonstrated is that chipping away at unjust systems can be helpful as we work towards transformation.” Gascón is walking a tightrope, she said: “How do you hold on to the principles that you say you believe in without losing your seat? And how do you balance the two?”
“Someone like me, I don’t believe in life without the possibility of parole. I don’t believe in ever trying a child as an adult,” Abdullah said. “But again, I’m not running for prosecutor.”
This article has been updated with a response, received after publication, from the campaign of Jeff Chemerinsky on his policy views.
Stay up-to-date
Support us
Bolts is a non-profit newsroom that relies on donations, and it takes resources to produce this work. If you appreciate our value, become a monthly donor or make a contribution.